




| Identification | Food & Medicinal Uses | Web Page Links | Online Videos | References |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| E.S. Shipp @ USDA-NRCS PLANTS Database | Leland J. Prater @ USDA-NRCS PLANTS Database | J.S. Peterson @ USDA-NRCS PLANTS Database | J.S. Peterson @ USDA-NRCS PLANTS Database | USDA PLANTS DB / Britton, NL & Brown 1913 | Steve Hurst @ USDA-NRCS PLANTS Database |
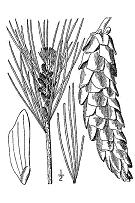
 The largest Northeastern U.S. conifer. Straight trunk with limbs growing horizonally out from the trunk.
Whorled, incremental braching (see video below). Blue-green needles, usually 2-1/2 to 5 inches long.
Only native pine in the Eastern U.S. that has 5 needles per bundle. Bark is smooth on
younger pines becoming furrowed on older pines. Cones are slender, thornless and long-stalked (4 to 8
inches long).
The largest Northeastern U.S. conifer. Straight trunk with limbs growing horizonally out from the trunk.
Whorled, incremental braching (see video below). Blue-green needles, usually 2-1/2 to 5 inches long.
Only native pine in the Eastern U.S. that has 5 needles per bundle. Bark is smooth on
younger pines becoming furrowed on older pines. Cones are slender, thornless and long-stalked (4 to 8
inches long).| Images from CalBerkeley | Images of young Eastern White Pines (by web page author) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|

|

|

|

|

|
|
The Pine Family (Pinaceae) As Wild Food with Frank Cook |
Food Sources of the Pine Family | Brewing Eastern White Pine Tea |
| 1 |

|
Native American Ethnobotany by Daniel E. Moerman Timber Press, c1998 ISBN: 0881924539 |
| 2 |

|
Medicinal and Other Uses of North American Plants: A Historical Survey with Special Reference to Eastern Indian Tribes by Charlotte Erichsen-Brown Dover Publications, c1989 ISBN: 048625951X |